SEBI Registered: Investment Adviser - INA000013323
| Name of the IA registered with SEBI: | The Alchemists Ark Pvt. Ltd. |
| Logo: |  |
| Trade/Brand Name of IA: | MoneyWorks4Me Investment Advisers |
| Brand Logo: |  |
| SEBI Registration Number: | INA000013323 Validity - May 16, 2019 - Perpetual |
| Registration: | Non-Individual |
| BSE Enlistment No: | 1187 |
| Address: | B-101, Signet Corner Building, Balewadi Phata, Baner, Pune, Maharashtra 411045 |
| Compliance officer Details: |
Name: Shrikant Jagtap Email: shrikant.jagtap@moneyworks4me.com Telephone: +919860359463 Address: Same as IA |
| Grievance Officer Details: |
Name: Mukta Vaze Email: mukta.vaze@moneyworks4me.com Telephone: +91 98609 19463 Address: Same as IA |
| Principal Officer Details: |
Name: Atharva Bhide Email: atharva.bhide@moneyworks4me.com Telephone: +91 91758 99463 Address: Same as IA |
| Standard Warning: | Investment in securities market are subject to market risks. Read all the related documents carefully before investing. |
| Disclaimer: | Registration granted by SEBI, enlistment with exchange and certification from NISM in no way guarantee performance of the intermediary or provide any assurance of returns to investors. |
Warning: Investment in securities market are subject to market risks. Read all the related documents carefully before investing.
Disclaimer: Registration granted by SEBI, membership of BASL (in case of IAs) and certification from NISM in no way guarantee performance of the intermediary or provides any assurance of returns to investors.
SEBI regional/local office address -
Address:
© 2026 The Alchemists Ark Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved. MoneyWorks4Me ® is a registered trademark of The Alchemists Ark Pvt. Ltd.

MoneyWorks4Me method for rating and ranking mutual funds for SIP
MoneyWorks4Me rating and ranking of funds for SIP is available to subscribers only. Moneyworks4Me is not a rating and ranking agency, however it is required that users have a way of selecting funds and building a Portfolio. The method used by it are described below to enable users to understand the logic behind the rating and ranking Subscriber will find more details on this in the various content made available from time to time. In case you need more please write to besafe@moneyworks4Me.com
MoneyWorks4Me rates and ranks mutual funds based on the following data-driven system:
- Performance Consistency: This is measure based on whether the fund has beaten the benchmark index consistently. For this we compare the 3-year rolling returns of the fund with the benchmark for a minimum of 5 years and preferable 10 years. The period of rolling is one month and holding period is 3 years. Fund are color-coded Green on Performance when the fund beats the benchmark more than 90% of the time. It is Orange if it beats 80% to 90% of the time and Red if less than 80%. Funds with less than 5 year data are color-coded Grey.
- Quality of Portfolio Holding: Moneyworks4Me has color-coded stocks as Green, Orange and Red based on whether the company's performance has generated a ROCE above a threshold level (cost of capital) over 10 years (minimum 6 years) and generated positive Free Cash Flow. For Banks it checks whether ROE is greater than 15% and sales has grown over previous year. Stocks that perform consistently on these combined metrics are color-coded Green (min score 14 out of 20), Orange (between 8 and 14) and Red (less than 8 out of 20). Fund are color-coded Green provided the portfolio has 70% holding in Green stocks but not more than 20% in Red stocks. Funds with more than 20% Red stocks in the portfolio are color-coded Red. The rest are Orange funds
Funds ranking in screeners: Performance Consistency and Quality are two parameters used for ranking funds for SIP. The ranking as follows GG, GO, GR, OG, OO, OR, RG, RO and RR.
With the same color-coded funds, the one with the higher Average 3-year rolling returns (over 5 to 10 years), the number that appears in the Performance tag, ranks higher.
Here is the summary:
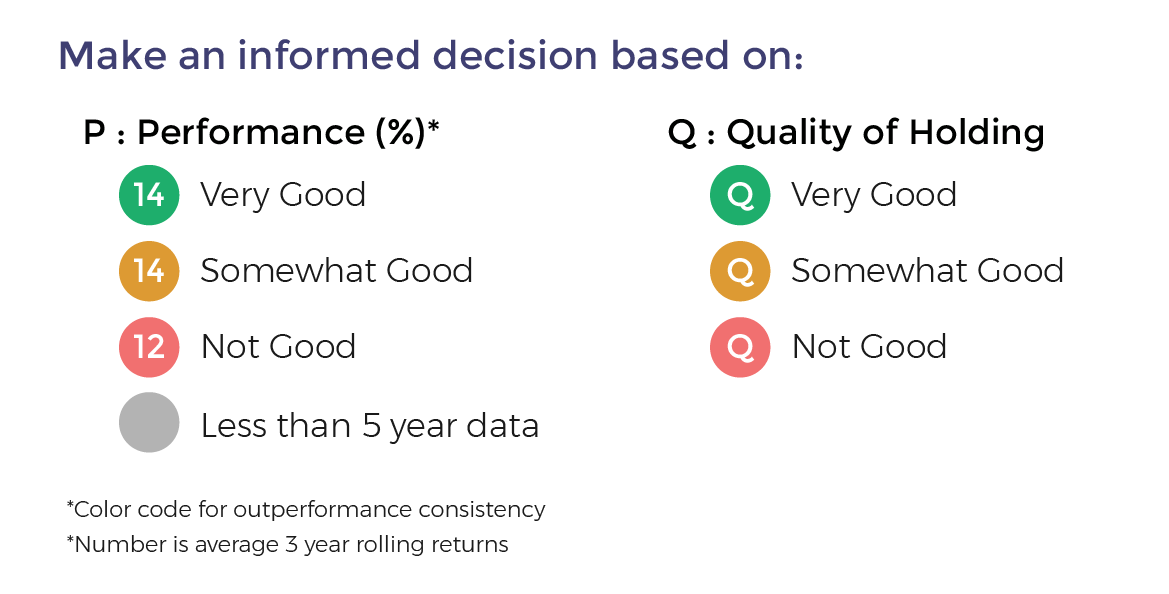
The third tag Upside Potential is not relevant for SIP. It is relevant for lumpsum investments in Mutual Funds.
Make an informed decision for Stocks
Invest using an intelligent system with powerful data-driven tools that help you identify opportunities and make informed buy-hold-sell decisions
Q Very Good
Q Somewhat Good
Q Not Good
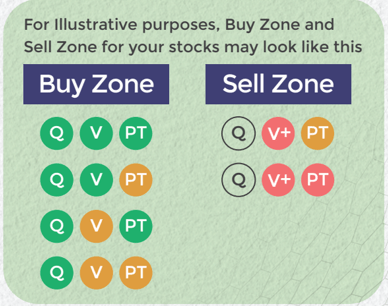
V+UnderValued (UV)
V Somewhat UV
V Fair Value
V Somewhat OV
V+ OverValued (OV)
Buy quality Stocks when they are available at reasonable prices and supported by an upward price trend and Sell when they are Overvalued using the Decizen Rating System. Covers 3500+ stocks
Make an informed decision for Funds
14 Very Good
14 Somewhat Good
12 Not Good
Less than 5 year data
Q Very Good
Q Somewhat Good
Q Not Good
*Color code for outperformance consistency
*Number is average 3 year rolling returns

Want to invest successfully in stocks?
How the heck do you select a solution that ensures it?
Check how good is your current solution!Does it get you focused on meeting your financial goals?

Does it get you focused on meeting your financial goals?
Investing is to means to funding your goals. Your solution must help you get clarity of your goals and how you should invest to reach them. Does your solution include Financial Planning?
Does it have a way of investing that you are confident will work for you?
Does it have a way of investing that you are confident will work for you?
Are you clear of the rationale behind recommendations?
Do you have a way of answering the most important questions: Which stocks are worth investing in, at what price and how do you build your portfolio?

Does it make it easy to find opportunities without wasting your time?

Does it make it easy to find opportunities without wasting your time?
- Are you spending too much time finding opportunities?
- Do you have a way of knowing when opportunities from your chosen set of stocks arise in the future?
- How confident are you about them?
Does it share the tools to enable decision making transparently?
Does it share the tools to enable decision making transparently?
Finally stock investing is all about make informed decisions.
Does your solution provide easy-to-use decision enabling data, information and tools?

Does it help you become a better investor

Does it help you become a better investor
- You will be investing for decades, for the rest of your lifetime.
- Does your solution help you learn what is required to invest successfully?
- Does it share knowledge and tools that you master as you invest?
Try MoneyWorks4Me Superstαrs - The complete solution for DIY Stock Investors

Do your Financial Planning

Invest using Quality-at-Reasonable-Price(QaRP)

Know the opportunities right

Invest with conviction
Read How the Heck to Invest and Reach Nirvana,

Portfolio
Sahi Hai?
DNA
of yourPortfolio!
Sher hai
ya Billi?
Take control of your financial future and start building your ideal portfolio today
- with reliable research at your fingertips.
Unlock the Power of Core Superstars Now →









