Whenever you think of Banks what comes to your mind? Your salary account, your savings account or if you are a businessman your current account. Maybe you are also thinking about loans you took from a bank - your home loan, your car loan or your personal loan. But, did you ever pause to think how does this industry actually work - What is the structure of the Indian Banking Industry? What is its business model? How does a bank make money? What is its future outlook? Let us demystify it in the next two ‘Industry Shastra’. Relax, we will not go much into its history or how the Indian Banking Industry evolved. In this first part, we will learn about its structure, its business model and then in the next part we will move to the past performance and future prospects.
The Banking industry plays a dynamic role in the economic development of a country. The growth story of an economy depends on the robustness of its banking industry. Banks act as the store as well as the power house of the country’s wealth. They accept deposits from individuals and corporates and lends to the businesses. They use the deposits collected for productive purposes which help in the capital formation in the country.
Today, the Indian Banking System is known the world over for its robustness. The Reserve Bank of India is the central/apex Bank which regulates the functioning of all banks operating within the country.
Structure of Indian Banking Industry
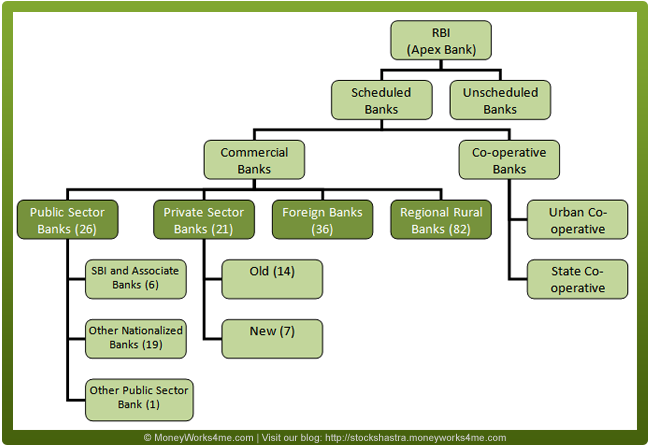
The banking system, largely, comprises of scheduled banks (banks that are listed under the Second Schedule of the RBI Act, 1934). Unscheduled banks form a very small component (function in the form of Local Area Bank). Scheduled banks are further classified into commercial and cooperative banks, with the basic difference in their holding pattern. Cooperative banks are cooperative credit institutions that are registered under the Cooperative Societies Act and work according to the cooperative principles of mutual assistance.
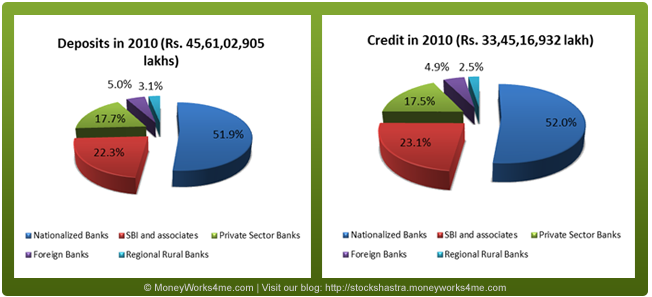
Major Players in the Indian Banking Industry
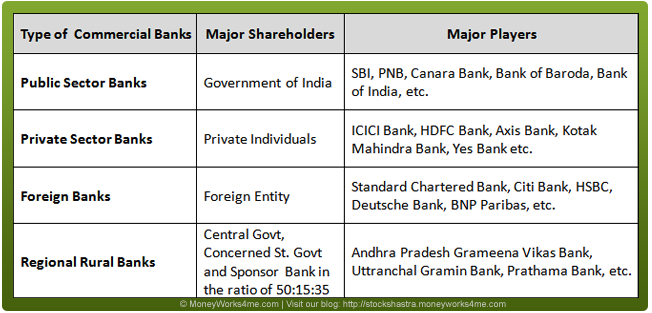
Public Sector Banks (SBI and associates + Nationalised banks) control more than 74-75% of the total credit and deposits businesses in India whereas Private Sector Banks around 17-18%.
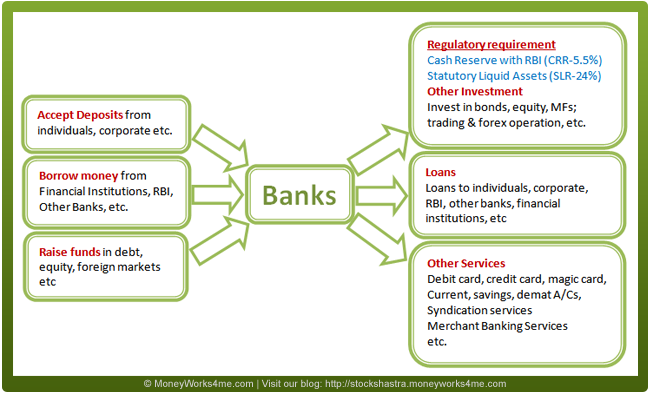
How does the industry work? Here is the analysis...
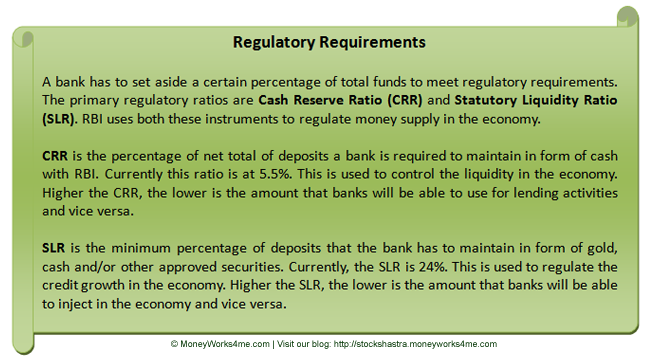
The banking industry in India is highly regulated. Few important regulations are mentioned in the diagram below:
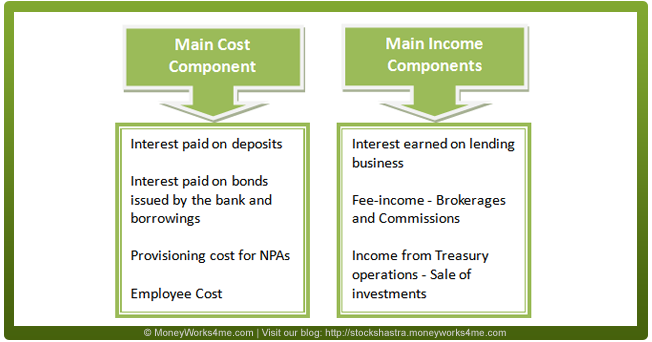
The core operating income of a bank is interest income (comprises 75-85% in the total income of almost all Indian Banks). Besides interest income, a bank also generates fee-based income in the form of commissions and exchange, income from treasury operations and other income from other banking activities. As banks were assigned a special role in the economic development of the country, RBI has stipulated that a portion of bank lending should be for the development of under-banked and under-privileged sections, which is called the priority sector. Current rules stipulate that domestic banks should lend 40% and the foreign banks should lend 32% of their net credit to the priority sector. On the cost sides, the major items for a bank are interest paid on different types of deposits, bonds issued and borrowings, and provisioning cost for Non-performing Assets (NPAs).
The banking business can be broadly categorized into Retail Banking, Wholesale or Corporate Banking, Treasury Operations and Other Banking Activities.
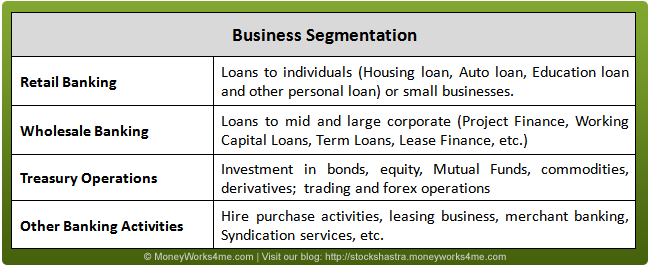
Retail banking segment is the highest margin business as compared to other business segments in the banking industry. Currently, ICICI Bank is the largest players in this segment in India. Other major players in this segment are SBI, PNB, HDFC Bank, etc. Wholesale banking segment in India is largely dominated by large Indian banks - SBI, ICICI Banks, PNB, BoB, etc.
A bank has to categorise its entire investment portfolio into three headings: Held-to-Maturity (HTM), Available-for-Sale (AFS) and Held-for-Trade (HFT). The investment categorized as HFT cannot be transferred to other categories. The investment, categorised as HTM can be transferred into AFS category and AFS to HTM category.
So far, we have discussed the structure and Business model of the Indian Banking Industry, which is entirely different from manufacturing and other businesses. For today, we stop here
So, see you next week with the second article on the Indian Banking Industry, where we will discuss its past performance, growth drivers, key concerns and the future prospects.
Already have an account? Log in
Want complete access
to this story?
Register Now For Free!
Also get more expert insights, QVPT ratings of 3500+ stocks, Stocks
Screener and much more on Registering.































Comment Your Thoughts: